As India races confidently towards its renewable energy goals, a silent revolution is unfolding behind the scenes: the rise of the large-scale batteries. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are rapidly moving from pilot projects to grid-scale deployment, acting as stabilizers for the country’s intermittent solar and wind generation.
A Prime example of this progress is Tata Power’s 100 MW solar farm in Chhattisgarh paired with a 120 MWh BESS – currently the largest combined solar-plus-storage plant in India.
These sophisticated battery systems are ingeniously designed to capture excess daytime solar power and dispatching it after sunset or precisely when needed. In doing so, these systems help deliver “round-the-clock” clean energy and enhance grid reliability. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the adoption of grid-scale batteries is not just beneficial, but absolutely essential to keep a renewable-heavy grid stable, handling effectively the hourly and seasonal variability in supply.
Storage Gap: How Far Is India from Its Targets?
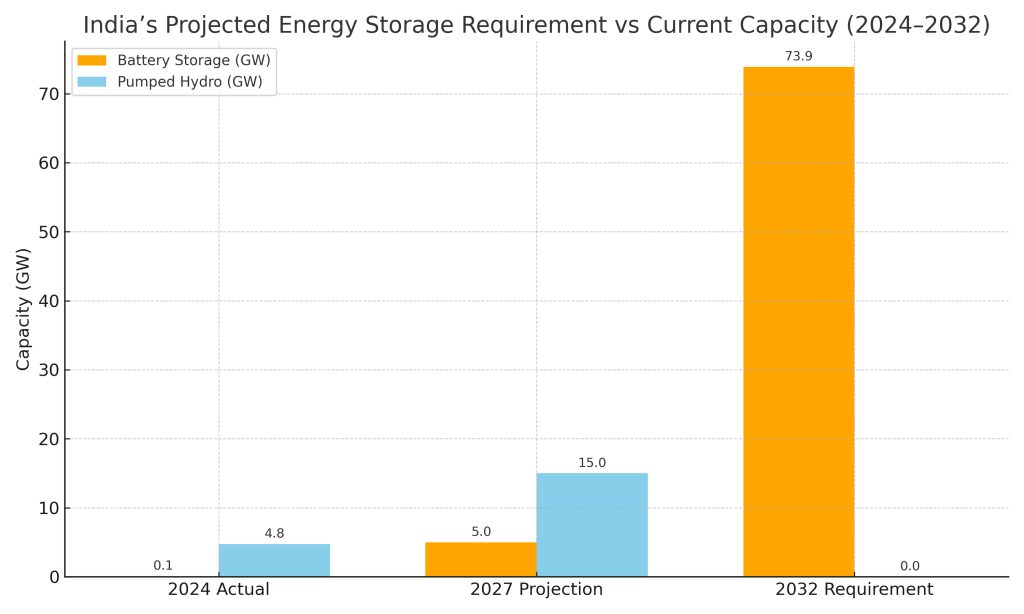
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that India’s energy storage market is still in its infancy. As of December 2024, the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) reports only 4.86 GW of total storage capacity, almost all pumped-hydro – with battery storage accounting for a mere 0.11 GW installed.
This is a mere fraction of what will be required to fulfill Our Country’s future energy demands and integration targets. The CEA’s own forecasts indicate that India will necessitate about 73.9 GW/411 GWh of storage by 2031–32 to integrate roughly 364 GW of solar and 121 GW of wind. In other words, hundreds of gigawatt-hours of batteries will be needed in the coming decade to smooth out renewable supply, regulate frequency and meet peak demand. Meeting this challenge means scaling up BESS capacity by orders of magnitude.
Energizing the Grid: Storage’s Role in Stabilization
The benefits of large-scale batteries are already evident on India’s grid. By intelligently absorbing surplus electricity generation and injecting power back into the system during deficits, BESS units performs:
- Peak-shaving
- Frequency regulation
- Black-start capabilities
that were traditionally the exclusive domain of conventional coal and gas plants. They can shave peaks by storing cheap power overnight or midday and using it during evening load, reducing expensive peak imports. Additionally, Batteries also provide fast reserve power and essential voltage support to prevent outages: A notable example is the approved 100 MW battery project in Mumbai will support hospitals, metro trains, the airport and data centers, islanding them during grid faults.
Moreover, by enabling solar projects to deliver electricity after sunset, storage is the cornerstone of “round-the-clock” (RTC) renewable power deals. In May 2020, ReNew Power won a 400 MW RTC tender by planning a hybrid plant with 900 MW of wind, 400 MW of solar and 100 MWh of battery backup – enough to commit 150 MW for 6 hours every evening.
Going forward, more hybrid projects will go online as a result of SECI’s ongoing RTC tenders, which pair renewable energy sources with storage, and rooftop solar bundling requirements. In practical terms, batteries are mitigating fluctuations and improving reliability on India’s grid. In order to ensure a more seamless integration of renewable energy sources, Tata Power states that its Mumbai BESS will “offer ancillary services including frequency regulation” and store surplus solar energy for peak use, ensuring smoother renewable integration.
These capabilities are especially important as India pushes for more renewable energy: experts warn that without storage, rapid solar/wind growth could force curtailment or put stress on the grid stability. A well-equipped battery fleet, on the other hand, can flatten net demand curves by absorbing midday solar oversupply and shifting it to the evening peak. In short, BESS systems enable the grid to use a higher share of “green electrons” without losing quality of supply.
BESS in Action: Major Indian Deployments
Major deployments are underway. Tata Power’s 100 MW/120 MWh solar-plus-storage plant in Chhattisgarh, and JSW Energy’s 125 MW/500 MWh standalone BESS in Kerala, are among India’s largest grid-scale storage projects. These systems offer dual charge-discharge cycles, making them ideal for supporting state grids and managing daily energy shifts.
Industrial users are also showing interest. Tata Steel, for instance, has committed to a 966 MW renewable power deal structured to provide 24×7 supply—something only possible with storage as a backbone. Meanwhile, the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) is securing long-term power purchase agreements at competitive rates, signaling that co-located battery and solar projects are becoming cost-effective.
Looking ahead, SECI has invited bids for multiple standalone and hybrid BESS projects, while rules for rooftop solar now envision significant battery pairing by 2030. Developers such as ReNew, Tata Power, and others are forming joint ventures to scale up battery manufacturing and deployment capacity locally.
Technology Evolution: Beyond Lithium-Ion
While lithium-ion batteries (Particularly Lithium Iron Phosphate and Nickel Manganese Cobalt chemistries) currently dominate the grid, India is diversifying. R&D efforts are advancing sodium-ion batteries, which make use of plentiful local resources like ore and salt. The market is also seeing the arrival of the Flow batteries, such as vanadium redox types, —ideal for long-term storage with no deteriorating over time.
For instance, Delectrik Systems has implemented modular flow batteries for microgrids and campuses. Gravity, solid-state, and zinc-air storage systems are additional cutting-edge choices that are meant to improve affordability, sustainability and duration. The goal is to match technology to application: lithium-ion for fast response, flow and sodium-ion for long use, and pumped hydro where geography allows.
Policy Support and Market Growth
This transformation is being propelled by Government support. A Viability Gap Funding (VGF) scheme now offers funding for up to 40% of BESS project costs, targeting 4,000 MWh of deployment by 2030. Another key policy—the PLI scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells, another will increase domestic supply by adding at least 50 GWh of new cell manufacturing capacity in India.
In order to guarantee that batteries are an integral part of renewable capacity, policy mandates now demand energy storage in all new solar projects. Financial incentives such as transmission fee waivers and tax exemptions on battery imports further enable these projects. The market has reacted favorably to this, showing a great deal of interest and forming alliances, such as the joint ventures between Fluence and ReNew to provide utility-scale storage.
According to India Smart Grid Forum (ISGF) and NITI Aayog projections, BESS capacity could increase from its current small base to 66 GW by 2032, opening up more than ₹5 lakh crore in investment opportunities. Storage is essential to India’s clean energy plans and is no longer an option.
Looking Forward: From Silent Stabilizer to Grid Hero
As India’s renewable capacity grows, batteries are becoming essential to energy security. Though still relatively expensive compared to traditional power sources, falling costs and shorter deployment timelines make BESS a smart investment. If India succeeds in building a strong battery ecosystem—from minerals to manufacturing to grid integration—it could achieve cleaner, more reliable 24×7 power, reduce energy waste, delay costly grid expansions, and cut carbon emissions.
Energy storage, a silent stabilizer or we can say a backroom player that makes sure the lights stay on regardless of the wind or the sun, will take center stage in India’s energy revolution in the upcoming years.



