As renewable energy is scaled up, the necessity for flexible, long-duration storage is rising. Battery excel in short-duration power delivery; hydrogen storage is ideal for bulk, seasonal storage. Together, both hybrid components offer a dynamic solution to stabilizing the grid. This article explores the synergy that hydrogen and batteries are creating in order to create future-proofed energy systems.
Why Combine Batteries and Hydrogen?
Batteries are well-suited to sub-hourly-to-daily variations—they quickly send energy for smoothing solar and wind fluctuations. Hydrogen storage, generated through green electrolysis, can be used for multi-day or seasonal requirements. It saves excess renewable generation for use when most required, covering longer-duration energy shortages.
Global & Market Trends
According to a recent market research report by BCC Research, the global hydrogen energy storage market is expected to experience explosive growth, soaring from US $1 billion in 2023 to an estimated US $23.7 billion by 2029. This demonstrates an incredible compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of just over 72%. The rapid growth substantiates the importance as a significant player in the future of clean energy storage as driven by investments, technology maturity, and government support throughout the world. 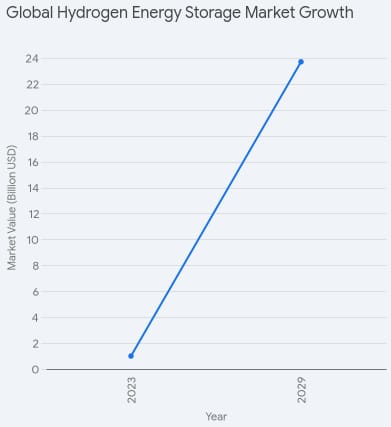
- Meanwhile, global grid-scale battery deployment is expanding substantially:
28 GW installed by the end of 2022, growing to nearly 970 GW by 2030 in the IEA’s Net-Zero scenario.
Hybrid Tech in Action
- Studies demonstrate hybrid battery-hydrogen microgrids cut operating expenses by 30% and loss-of-load occurrences by 80% through sophisticated, prediction-free optimization techniques.
- PEM electrolysis-fuel cell microgrid models providing continuous, dispatchable renewable energy work in harmony, balancing surpluses and deficits effortlessly.
- IRENA predicts an 86% cost decrease for hybrid energy storage as technologies improve.
The Indian Context
- India aims to reach 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030, which will fuel the need for long-duration storage and grid stability.
- India, under the National Green Hydrogen Mission, is also aggressively pursuing high electrolyzer deployment; its renewable build-out plan sees 125 GW powering 5 MMT of green hydrogen by 2030.
- Pilot strategies nationwide are considering hybrid systems—particularly off-grid and industrial cluster combinations with solar and batteries.
- The hydrogen storage industry in India has been developing tremendously fast in line with India’s objective to become a global green hydrogen hub. As indicated by RationalStat, the Indian hydrogen gas storage market valued USD 101.9 million in FY 2023 is anticipated to grow rapidly to USD 286.5 million between FY 2023 and FY 2031, with a CAGR of 13.8%. This growth is supported by the National Green Hydrogen Mission, which earmarks ₹19,744 crore (USD ~2.4 billion) for green hydrogen production and the ecosystem, including storage. The government’s goal is to produce 5 million metric tonnes (MMT) of green hydrogen annually by 2030, which is expected to spur demand for safe and scalable hydrogen storage solutions. Numerous companies are positioning themselves. Domestic company INOX CVA is developing unique technologies to advance cryogenic and compressed hydrogen tanks. Many public and private sectors companies, including BPCL–Sembcorp, Larsen & Toubro, ReNew Energy Global, and Adani New Industries, are investing in integrated hydrogen infrastructure to include generation, storage, and consumer delivery. Matrix Gas and Renewables (a subsidiary of Gensol Group) has also announced plans for 1GW green hydrogen projects. Likewise, globally established players such as Air Liquide, Linde, and Hexagon Composites have initiated regional plans to increase their hydrogen storage technologies into the Indian market. ransformative growth.
Tech Challenges & Integration
- Energy Management Systems (EMS) are assets in coordinating the varying states of charge of batteries with hydrogen electrolyzers and fuel cells to achieve the maximum output of hydrogen.
- When it comes to system integration, the design of power electronics, balancing efficiency, and integrating variable renewable sources were described as challenges.
- Safety, maintenance, and CAPEX are major issues—but frameworks developed through research/programs (i.e., hydro-battery sizing and optimizing EMS) are reducing these gaps.
Policy & Market Levers
- India’s Green Hydrogen Mission and green hydrogen policies at the state level are creating encouragement for hybrid installations.
- Internationally, the electrolyzer risk of deployment is lowered also with aligning battery storage subsidies (e.g., IRA in the USA) to hydrogen incentives.
- Good standards and certification efforts will support confidence for deploying large-scale H2 + BESS systems, which are both coming down the pipeline
Roadmap Ahead
- Indian pilot projects, especially in remote microgrids or industrial clusters, could demonstrate hybrid success.
- Innovation in materials (e.g., metal hydrides or liquid organic hydrogen carriers) and power management will increase energy density and safety.
- Financial models bundling batteries and hydrogen could unlock superior techno-economic returns compared to standalone systems.
Hybrid battery-hydrogen energy systems represent a compelling advancement in energy storage, offering rapid response and long-duration flexibility. With hydrogen storage projected to grow at a 72% CAGR and battery storage surging by almost 35-fold by 2030, these systems are poised to transform India’s grid resiliency. As the nation advances its renewable and green hydrogen goals, leveraging hybrid solutions could ensure a smarter, cleaner, and future-resilient energy ecosystem.



